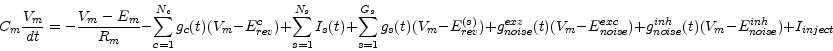CbStOuNeuron
Subsections
The membrane voltage V m
with the following meanings of symbols
C m E m R m N c g c t )c E rev c c N s I s t )s G s g s t )s E rev (s ) s
g noise exz t )
E noise exc
g noise inh t )
E noise inh
I inject
At time t =0V m V init
The value of E m V m
If the membrane voltage V m V tresh CbNeuronSt sends a spike to all its outgoing synapses and the membrane voltage follows a predefined spike templage during the absolute refractory period of length T refract if doReset = 1 .
If the flag doReset=0 the spike template is not applied and the above equation is also applied during the absolute refractory period but the event of threshold crossing is transmitted as a spike to outgoing synapses. This is usfull if one includes channels which produce a real action potential (see HH_K_Channel and HH_Na_Channel ) but one still just wants to communicate the spikes as events in time.
The exponential Euler method is used for numerical integration.
ge (S exc and inh conductances (noise)
gi (S exc and inh conductances (noise)
ge0 (S exc and inh mean conductances (noise)
gi0 (S exc and inh mean conductances (noise)
tau_e (S time constants and std for exc and inh conductances (noise)
tau_i (S time constants and std for exc and inh conductances (noise)
sig_e (S time constants and std for exc and inh conductances (noise)
sig_i (S time constants and std for exc and inh conductances (noise)
Ee (V Reversal potential for exc and inh currents (noise)
Ei (V Reversal potential for exc and inh currents (noise)
STempHeight (Volt Height
Vthresh (V If V m V thresh
Vreset (V The voltage to reset V m
doReset (flag Flag which determines wheter V m
Trefract (sec Length of the absolute refractory period.
nummethod (flag Numerical method for the solution of the differential equation: Exp. Euler = 0, Crank-Nicolson = 1
type :Type (e.g. inhibitory or excitatory) of the neuron
Cm (F The membrane capacity C m
Rm (Ohm The membrane resistance R m
Vresting (V The resting membrane voltage.
Vinit (V Initial condition forV m t =0
VmScale (V Defines the difference between Vresting and the Vthresh for the calculation of the iongate tables and the ionbuffer Erev.
Inoise (W 2 Variance of the noise to be added each integration time constant.
Iinject (A Constant current to be injected into the CB neuron.
Em (V The reversal potential of the leakage channel
Vm (V The membrane voltage
OuInoise :noise input current
OuGnoise :noise input conductance
Isyn :synaptic input current
Gsyn :synaptic input conductance
nIncoming :Number of incoming synapses
nOutgoing :Number of outgoing synapses
nBuffers :Number of ion buffers
nChannels :Number of channels